One of the core problems of blockchain technology is that different blockchains cannot interact smoothly, and their cryptos are isolated inside the designated networks. Polkadot was designed to solve this problem and take blockchain interoperability to a new level. In this article, we will discuss how Polkadot’s technology aims to upgrade the blockchain. We will also review the Polkadot ecosystem’s architecture and determine whether its native coin, DOT, is a good investment.
Key Takeaways
- Polkadot Network seeks to make blockchain a full-scale practical application.
- The blockchain was founded by one of the Ethereum co-founders.
- Polkadot is a multi-chain environment.
- Its architecture is coordinated by a central Polkadot Relay Chain, connecting Parachains, Parathreads, and Bridges.
- Polkadot has its token, DOT token that can be used for staking.
What Is Polkadot?
Polkadot is a network that unites blockchains into a single space where users can create their blockchains (so-called parachains) and process and exchange data from various blockchains.
Polkadot was created to simplify the creation of custom blockchains for developers for their projects. It is a technology designed to increase the interoperability of different blockchains, such as BTC and ETH, and combine them within a single multi-blockchain.
Polkadot aims to solve the fundamental problems preventing blockchain technology from becoming a full-scale practical application:
- Scalability – so-called first-generation blockchains cannot process the enormous amount of transactions in the future decentralised world. Network nodes currently process transactions in a one-on-one format, which hinders the further growth of the network.
- Isolation – blockchains remain discrete and independent, lacking two-way communication and interoperability.
Polkadot serves as a base for other cryptocurrency projects. It goes even deeper than Ethereum, a different kind of blockchain. Polkadot is a type of blockchain called Layer 0, while chains like Ethereum, Solana (SOL), or Cardano (ADA) are called Layer 1 blockchains.
Polkadot is based on the Proof-of-Stake consensus protocol that implies that validators use tokens placed as a guarantee to determine the next block in the chain. This differs drastically from the Proof-of-Work protocol used in earlier blockchains like Bitcoin or Litecoin; in PoW, blockchain miners solve cryptographic puzzles to add new blocks to the chain and receive DOT rewards for doing so.
The network’s name reflects its concept: polkadot is a pattern on fabric with big circles or dots of the same size. The circles represent various blockchains and the overall design of the Polkadot cryptocurrency ecosystem.
Polkadot has designated wallets that can be used for storing your assets, staking, exchanging DOT tokens, and multiple DeFi services. Polkawallet is available as an Android and iOS application and browser extension. You can select a Polkawallet among many wallets included in the ecosystem.
Polkadot’s ecosystem also comprises various explorers for real-time monitoring and performance of the networks. Thus, you can search, analyse, and visualise the blockchains on the Polkadot network via the Polkadot Explorer.
A Brief Glance Into The History Of Creation
Polkadot was co-founded by Gavin Wood, who was also one of the co-founders of Ethereum and former CTO of the Ethereum Foundation.
The original whitepaper was released in 2016, and following a successful $145 million fundraise a year later, Polkadot finally went live with its initial mainnet in May 2020.
Initially, the network was managed by the Web3 Foundation, but later on, the governance transitioned to DOT token holders and was no longer controlled by a centralised entity.
The mainnet launch built on the success of the alpha release of its sister network, called Kusama, in 2019, described as a canary network and live proving ground for Polkadot’s technology and functionality.
Polkadot is now moving into the next stage of core infrastructure development, including the Parachains auction rollout, Parathreads, and cross-chain message passing.
How Does Polkadot Work?
Polkadot is a network protocol allowing you to transact data (not just tokens) between blockchains. This makes the network a multi-chain environment.
Thus, in the Ethereum network, the register distribution occurs between users only inside this network, while in Polkadot, the information is stored on devices operating on all networks integrated into this protocol.
Polkadot’s architecture is coordinated by a central Relay Chain, connecting Parachains, Parathreads, and Bridges.
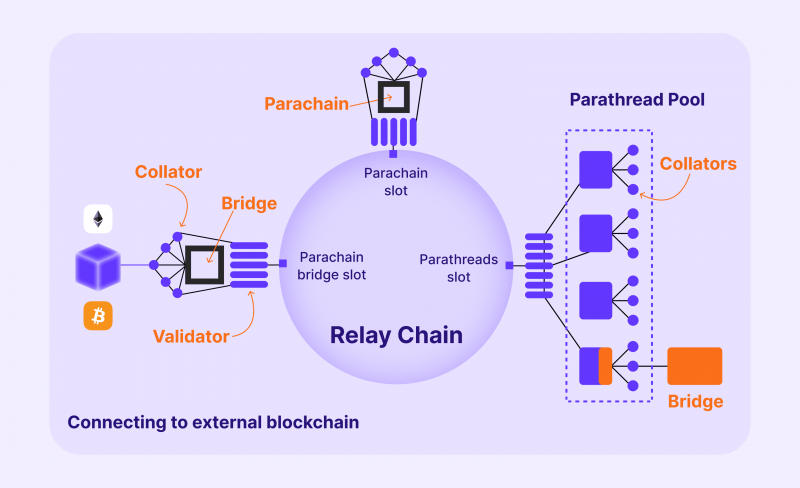
The Relay chain enables the chains of blocks on the Polkadot platform to interact. It is a base protocol used as a framework for developing other blockchains in the Polkadot ecosystem. The relay chain is not designed to support smart contracts and acts only as a coordinator and communicator between different blockchains. The relay chain’s protocol determines the shared security of the network, as well as cross-chain functioning and consensus.
Polkadot parachains (short for parallelised chains) are autonomous blockchains in the Polkadot ecosystem, and each of these blockchains has its tokens, governance and rules for transactions. Developers can create and run their parachains to support their applications. Parachains have the security and networking benefits of the relay chain because they are connected to it. The Polkadot relay chain also allows the communication and interaction of parachains. The relay chain enables parachain’s system to work seamlessly while developers and users can focus on other specific goals like privacy or scalability and their particular applications.
Bridge Chain (or Bridges) connects blockchains that do not use Polkadot governance protocols (for example, Bitcoin, Ethereum and Tezos blockchains).
Parathreads network performs the same functions as Bridges; however, it operates on a pay-as-you-go model that allows them to work when needed and does not require a permanent connection to the relay chain.
Some other essential components support the work of the Polkadot system.
Thus, parachains are built by so-called collators: they collect user transactions and confirm blocks based on the Proof-of-Validity algorithm (validity proof). Collators receive a reward for their work. The amount of the compensation depends on the specific parachain. The activity of collators is similar to miners’ work in blockchains with Proof-of-Work and Proof-of-Stake algorithms.
Collators pick transactions from parachains and pass them to the relay chain validators. Validators process transactions just like miners in the Bitcoin network. Validators secure the network by staking DOT to run validating nodes and perform full verification of the Relay Chain. They also validate Parachains and take part in consensus with other Validators to agree on the true shared state of the network, rejecting any invalid transactions. They add new blocks to the Relay Chain, and, as a result, all parachains share in its security, receiving incentive rewards in return.
Validators receive their tokens from nominators. They pay a deposit for validators, which is taken away from them if the activity of the validators does not comply with the rules of consensus.
Nominators do not participate in the process of making and confirming transactions. Security nodes monitor violations by validators, the so-called fishermen: they identify cases of illicit behaviour, create evidence containing data on conflicting validator votes, and receive a share of the confiscated bets of violators.
This architecture of the blockchain network has received recognition in the cryptocurrency world. According to many experts, it provides a higher level of security and is one of the most consistent mechanisms in the market.
Users of Polkadot can influence the development of the software.
Thus, ordinary DOT holders are anyone who purchases DOT tokens. They can use their DOTs to propose changes to the network and approve or reject significant changes proposed by others.
The Council consists of members elected by DOT holders. These users propose changes and determine which changes are implemented to the software.
The Technical Committee comprises teams actively building Polkadot. They are entitled to make special proposals in case of an emergency. The Council members elect members of the technical committee.
Polkadot Token
DOT is Polkadot’s native token. It is used to make payments, participate in network management, pay fees and staking. DOT holders can vote on important network management decisions. DOT can also be used to motivate validators to validate transactions on the Polkadot network.
DOT can also be used in applications built on Polkadot blockchains. DOT tokens are the main transaction currency in such applications, which can span various industries.
The circulation supply of Polkadot is $5,428,281,037.22, and its market capitalisation is 1,214,870,702 DOT. This means you can buy or sell tokens to make a profit. The token is traded on Kraken, Binance, and other major crypto exchanges.
How To Stake DOT
The network utilises the Nominated Proof-of-Stake mechanism to validate transactions. This mechanism involves staking — locking up some DOT tokens to get profit.
If you have DOT, which is Polkadot’s network token, you can participate in voting for Polkadot blockchain proposals, rent parachain slots, and receive crypto rewards for staking on Polkadot to help verify network transactions.
When you stake Polkadot, you give your DOTs to a validator. You are betting that the validator you select correctly verifies transactions on the network. A validator is a special server that uses special software to suggest and check a group of transactions.
Validators who properly validate transactions get more DOT tokens. These tokens are given to the investors who have put their money into the validators. Any validator who tries to verify fraudulent transactions is punished by losing their staked DOT.
There are several ways to stake your DOT coins. You can stake the tokens on the exchange such as Kraken or Gemini. This is the easiest way that is ideal for beginners.
Another option is staking with the wallet using a Polkadot.js Chrome extension. This extension works on Chrome, Vivaldi, Edge, and other Chromium-based browsers.
You can also stake by running your validator node. However, if you choose this option, you must have a profound knowledge of technology and robust equipment, take care of maintenance, and consider the energy required for staking.
You can earn rewards in exchange for putting your DOT tokens at risk. DOT staking can bring you relatively high yields; however, staking with Polkadot can be challenging. Potential returns for staking DOT with a validator on Polkadot is about 14.8% while staking with an exchange is around 10% to 12%.
How To Invest In Polkadot
DOT, a Polkadot coin, is a relatively new token in the crypto market; therefore, it often raises the question, “Is Polkadot a good investment?”.
It was first launched in 2020 at $2,94; however, by the end of 2021, it was traded at $54,98. Though now the Polkadot price is only around $5, some experts believe that this fall can predict a significant price boost in the future. Thus, some analysts predict that by 2030, the coin will reach its maximum of $83,42.
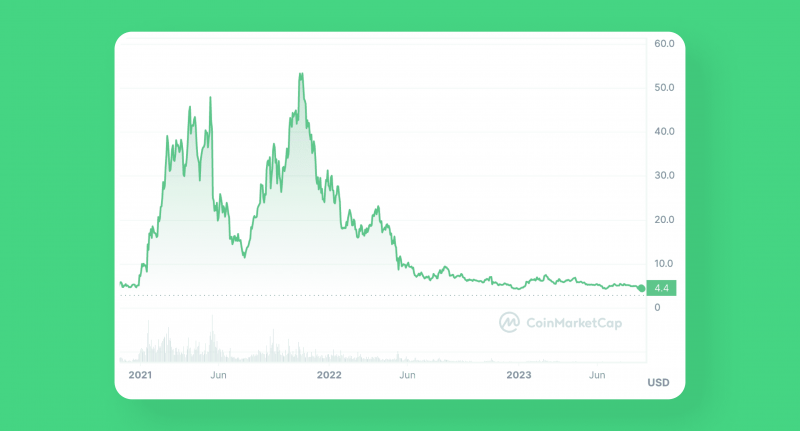
For now, the Polkadot token is among the top 15 cryptocurrencies in the Coimarketcap ranking. Moreover, it is considered the 11th cryptocurrency by market cap according to the Coinbase explorer.
More and more crypto investors are looking for a solution that will allow them to link to multiple blockchains from one platform, and Polkadot can be such a solution.
The DOT coin is currently worth just $5 but has explosive upside potential. This means that buying this cryptocurrency now at a lower price can be very beneficial since it will bring you significant returns in the future when its price rises.
Pros & Cons
Pros
Among the positive features of the Polkadot ecosystem and its token, DOT, we can name the following:
- It is an innovative model with promising prospects that allows multiple independent blockchains to communicate with one another regardless of the network the chain is created on.
- The Polkadot protocol accommodates both economic and transactional scalability. Economic scalability is achieved by enabling the same validators to secure multiple blockchains, while the transactional one is guaranteed using transactions spread across multiple parallel parachains.
- The network is easily upgradeable as new technologies are available without a hard fork.
- All Polkadot stakeholders can actively participate in the network management.
- Polkadot shows a very high level of security and good network scalability.
- It has open-source code, which is an advantage for developers.
Cons
However, there are also some disadvantages:
- Since DOT is a relatively new token, it lacks an established track record.
- Polkadot faces a high degree of competition in terms of decentralised applications. Major networks like Ethereum, Tron, or Binance Smart Chain are among the main rivals.
- Since the project is relatively new, it is not yet completed, and some technical aspects are still under development.
Conclusion
Polkadot is a new-level blockchain that makes network security collaborative instead of competitive. The Polkadot ecosystem aims to resolve many limitations that blockchains encounter, such as security degree and cross-chain interoperability. The Polkadot’s native token, DOT, might be a profitable investment since it has a great potential for price uprising. Considering the overall benefits for investors and developers, it will be interesting to follow Polkadot’s evolution.
FAQs
Where to buy Polkadot (DOT)?
The Polkadot coin can be purchased at major crypto exchanges like Binance, Kraken, or Coinbase.
What is the future of Polkadot?
Long-term forecasts for the Polkadot rate are optimistic. However, digital assets are very volatile, and predictions are often wrong.
What is DOT used for?
In addition to the value transfer function, Polkadot network tokens are used to vote in parachain auctions, nominate validators and vote on project development suggestions.











