Along with the emergence of crypto technology and the development of crypto trading, there is an urgent need for a place to store digital valuables, as well as other important transactions. For this task, crypto digital wallets were created, which are the receptacles of unique addresses that are inherent to each coin. Contrary to popular belief that crypto is stored in a wallet, this is actually not the case.
In this article, we will understand what is a crypto wallet, crypto address, and what are the main differences between them. You will also learn what variations of digital wallets and addresses exist.
Key Takeaways
- To date, there are 4 different formats for Bitcoin addresses that have advantages and disadvantages and can be used within a particular blockchain.
- Today, there are 2 types of crypto digital wallets – cold and hot, subdivided into different types and having different principles of work.
What is a Crypto Wallet?
Blockchain wallets are online platforms that provide storage services for digital currencies. In addition to enabling the purchase and sale of cryptocurrencies, these services also facilitate exchange transactions and payment for goods and services. There are a variety of crypto wallet options available from digital money issuers and third-party resources specializing in working with different currencies. Cryptocurrency wallets contain the public and private cryptographic keys of their owners, allowing them to work with crypto currencies such as Bitcoin, Doge, Bitcoin Cash, and others.
Today, a large variety of crypto storage of distinct kinds are divided into 2 categories – cold and hot. Hot wallets store private keys to access cryptocurrencies inside applications connected to the Internet. At the same time, cold wallets keep them offline, that is, outside the Internet. Many in the crypto industry believe that hot wallets are insecure because of their nature; all digital wallets store your private key and codes on their online servers, which are at risk of breakage, hacking, and other malicious actions, while cold wallets don’t have this drawback because all transactions take place outside the Internet, where fraudsters have no access to investors’ assets.
What is a Crypto Address?
Whether it is Bitcoin or an Altcoin, a crypto wallet address is a unique sequence of different upper and lower case letters and numbers that acts as an identifier or the exact location of crypto in each individual blockchain, which is necessary to perform any financial transactions with them, whether they are deposits, withdrawals, or transfers. Depending on the coin, the number of characters of such an identifier can be from 27 to 40. For example, the Bitcoin wallet addresses most often use a sequence of 26–35 characters and consist of both letters and numbers.
The process of generating a Bitcoin address is as follows. First, a private key, a completely random set of characters, is created in your wallet. Based on the private key, a wallet’s public key is calculated by hashing. The crypto address is created, already based on the public key, by several transformations.
The public code is generated again with each new financial transaction. This mechanism is integrated to increase the security of crypto-assets. At the same time, the “old” keys remain in the user’s archive and do not lose their activity – that is, if someone transfers funds to a previous address, the recipient’s balance is replenished. By the way, there is an option to disable the generation of new addresses. However, by activating it, the user allows interested third parties to trace the entire history of their own financial transactions on a fixed (unchanging) public key.
What is the Difference Between Them?
Despite the fact that a crypto currency wallet and crypto address are two inseparable elements that are basic for making crypto transactions using different digital assets, there are multiple differences between them.
First of all, it must be understood that contrary to the common belief of most that crypto assets are stored in a crypto wallet, this is a misconception that often misleads crypto enthusiasts. A crypto wallet is a place where a new address is generated for each individual digital asset, with transactions occurring both within the same blockchain and across different blockchains. Between the process of using a crypto wallet to store a particular coin at a crypto address tied to it, we can draw an analogy with a keypad that acts as a wallet and keys that are multiple addresses within the wallet. Thus, with one crypto wallet, an investor has access to hundreds of crypto addresses corresponding to each crypto coin stored inside the crypto wallet.
Currently, not all cryptocurrency wallets contain private keys. For example, there are only coin wallets that are only used to check balances and verify transactions. They don’t contain a private key, so you can’t sign a transaction, i.e., send those coins from that wallet. There are also exchange wallets and some online wallets where you do not control the private keys; they are controlled by whoever controls the exchanges.
Of all types of digital storage, the coldest type of hardware-type wallet is considered the safest, and only the owner has access to it. Among all Bitcoin addresses, SegWit is considered the most common and popular format.
Different Types of Wallets and Addresses
The popularity of cryptocurrency technologies has become a big impetus for the development of solutions that are aimed at creating a special ecosystem that allows you to carry out a wide range of operations with crypto assets, including deposits, withdrawals, and transfers from one address to another. Crypto wallets have become a real revolutionary solution offering a new format for interacting with digital money.
Today, there are two categories of crypto wallets – hot and cold, each of which includes different subtypes of wallets, such as software, online (web), desktop, mobile, hardware wallet.
Crypto wallets come in a variety of types, as do crypto addresses, each of which has its own characteristics. Bitcoin wallet addresses generally fall into four categories:
1. Segwit or Bech32 (P2WPKH) Address
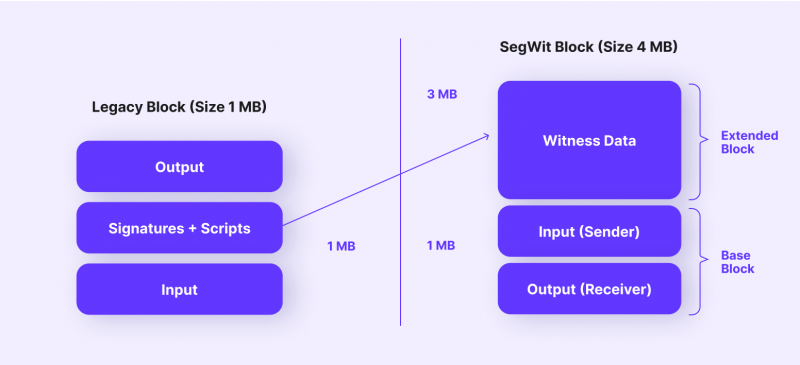
This is an advanced type of address used to reduce the size of distributed ledger blocks to speed up transaction response time. Addresses start with “bc1” and are longer than P2PKH and P2SH. Bech32 is a native Segwit addressing format (though P2SH can also be a Segwit address), so usually, when talking about using Segwit addresses, it means Bech32. The advantage is the lowest commission for sending transactions and high processing speed. The disadvantage is that only some wallets and systems support it.

2. Legacy or P2PKH Address
This address format is the first version of a Bitcoin address that begins with a “1” and has 26 to 36 characters. The average fee when sending from a P2PKH address is frequently higher than when sending from a Segwit address because transactions with legacy addresses are larger.
3. Compatibility or P2SH Address
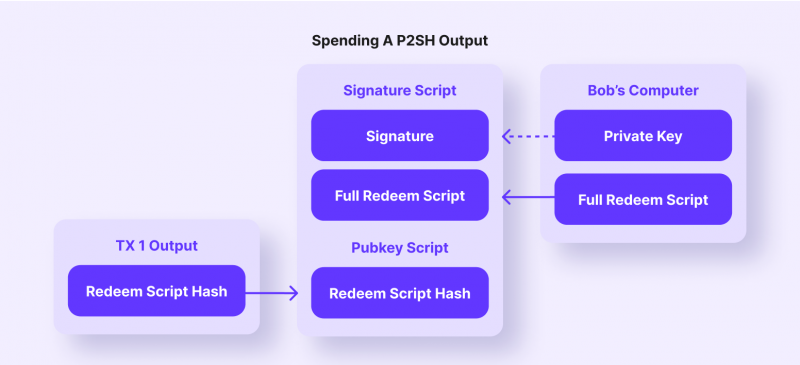
The new address type is structured similarly to P2PKH, but starts with “3” instead of “1”. P2SH provides more complex functionality than past address types. To spend BTCs sent via P2SH, the recipient must provide a script that matches the script hash and data, making the script valid. However, all the average user needs to know is that using this address type instead of P2PKH will lower the average transaction fee.
4. Taproot or BC1P Address
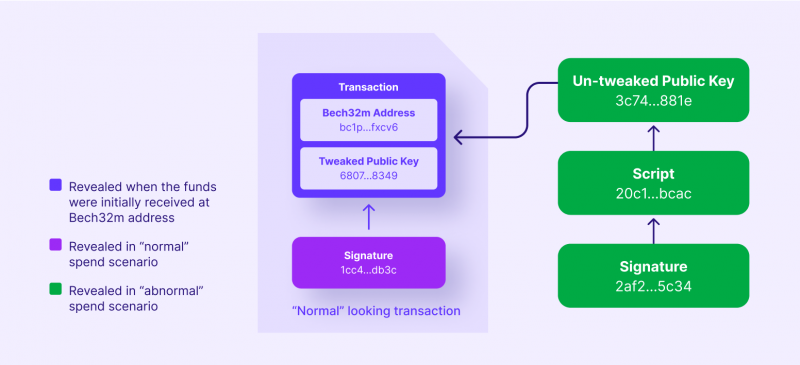
This format results from the most current and significant update to the Bitcoin network since the SegWit improvement in 2017. The main advantage of Taproot addresses for their owners is the lowest fees compared to other formats. Among the disadvantages is the low prevalence, as this format is currently supported by a few wallets.
Conclusion
In order to summarize all said above, it should be said that each crypto wallet is a repository of a large set of addresses to enable various financial transactions with available crypto assets, be it deposits, withdrawals, or transfers. Unlike Ethereum addresses, Bitcoin addresses have more varieties and, therefore, greater coverage because each wallet, regardless of type, whether cold or hot, supports only certain formats that have more than one difference in architecture and operation.